What is Hypodontia?
Hypodontia or Congenitally Missing Teeth is a form of dental agenesis, which is a condition characterized by some of the teeth being missing from birth. In other words, the teeth never develop. There are several forms of dental agenesis- hypodontia refers to up to 6 missing teeth, not counting wisdom teeth. Anyone can be born with it, though genetics seem to be a factor. Approximately 2% to 8% of the population is impacted by this condition.
Hypodontia can involve any of the teeth, but the ones that are primarily affected include:
- Upper lateral incisors: smaller teeth on either side of the upper 2 front teeth
- Upper second premolars: teeth just in front of upper molars
- Lower second premolars: teeth just in front of lower molars
Can Congenitally Missing Teeth affect my oral health?
Yes, hypodontia can have an impact on your oral health. It can cause inadequate jawbone growth and gum damage, which can cause the jaw to be underdeveloped, making it appear smaller than it should be. In addition, missing teeth can impact your ability to eat and speak as well as brush and floss your teeth.
What are the Common Symptoms of Congenitally Missing Teeth?
The primary symptom of hypodontia is missing 1 to 6 teeth. This condition can impact any of the teeth, except the wisdom teeth, and can impact the primary or permanent teeth. In some cases, patients with hypodontia have teeth that are smaller than average or peg-shaped- and due to the missing teeth, have spaces between their teeth.
In some cases, hypodontia is a symptom of another genetic disorder and some patients with hypodontia develop symptoms of ectodermal dysplasia, such as:
- Thinning hair
- Poor hearing and/or vision
- Nail abnormalities
- Lack of sweat glands
Common Causes of Congenitally Missing Teeth
Typically, patients with hypodontia have an abnormality that impacts the dental lamina, which is the band of tissue under the gums where the teeth form. Most of the time, genetics are involved, but there are other factors that could cause this condition as well.
Hypodontia is considered a birth defect, but may also be caused by certain illnesses, infections, or treatments during the tooth development phase such as:
- Cleft lip/palate
- Genetic disorders including ectodermal dysplasia or Down Syndrome
- Low birth weight
- Chemotherapy/radiation
- Infectious diseases such as rubella or candida
Common Treatments for Congenitally Missing Teeth
There are several options for treating congenitally missing teeth, including:
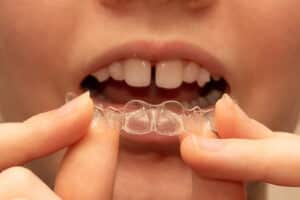
Braces/Orthodontics
Braces can straighten crooked teeth and close small gaps between teeth. Braces work by putting pressure on the teeth to push them into their appropriate position.
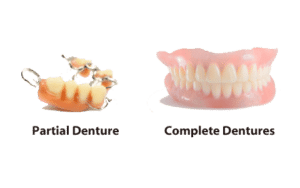
Dentures
Conventional dentures are typically made of an acrylic base and porcelain teeth. It sits on the gums, replacing the missing teeth. This prosthetic must be removed at night for cleaning and to allow the gums to rest. Dentures must be relined or replaced every few years due to changes in the gum and jawbone structure.
Bridges
A dental bridge is designed to replace several missing teeth in a row. A traditional bridge is secured to the adjacent teeth on either side of the gap. Dental bridges typically last up to 10 years, but may last up to 20 with proper care and maintenance.
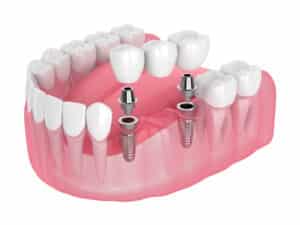
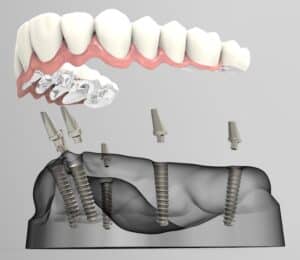
Dental Implants
A dental implant is a device made of 3 pieces that is implanted into the jawbone to create a stable base for replacement teeth. A single dental implant can be used to replace a single tooth, while multiple implants can support up to an entire arch of missing teeth. A dental implant is designed to last a lifetime.
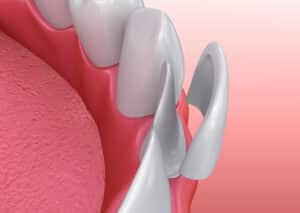
Bonding and Veneers
Dental veneers are a cosmetic procedure designed to restore the appearance of the upper front teeth. They are thin shells that are cemented to the front teeth. In most cases, some of the enamel must be removed to create space for the veneers. Dental veneers usually last for about 7 to 10 years with proper care and maintenance.
Dental bonding may also be used to build up teeth, restoring their appearance. Bonding usually must be repeated every 3 to 5 years.
Frequently Asked Questions about Hypodontia
If you have questions or concerns about congenitally missing teeth, talk to a dental professional. A couple of the most common questions include:
Is congenitally missing teeth a rare condition?
Yes, congenitally missing teeth is a fairly rare condition, with only around 2% to 8% of the population being affected.
What is the typical age for treatment of congenitally missing teeth?
Dental implants and veneers are typically reserved for adults over the age of 18. However, other treatments may be used after all of the teeth have erupted.
Can congenitally missing teeth impact self-esteem?
Yes, congenitally missing teeth can have an impact on your self-esteem. However, treatments can restore your appearance and self-esteem.